The Cost of Beer Labels: How Does Commercial Pricing Work for Professional Beer Labels?
The immediate answer to that question is, it depends. There simply is no quick answer to how much beer labels cost because every project is so different. Instead, it’s important to have a general understanding of how commercial beer label pricing works and all the factors that can impact the cost of your project.
How Craft Beer Labels are Priced
The main reason why it’s tough to provide a quick custom beer label estimate is that each project is a custom process. Each order is manufactured from scratch, so there are no pre-made products to ‘save’ cost with. Every beer label features an original design and uses different materials per your specifications. At Blue Label, we rarely see a project cost less than $150 total (simply due to the costs associated with setting up equipment) and will scale up depending on your specifications.
Once you do get a beer label estimate, it’s also important to evaluate your investment in understandable numbers. While some people may want to break down cost on a price per unit basis, we find that it’s generally better in print to evaluate your label cost per thousand pieces. This perspective allows you to avoid the fractional cents in per unit costs and helps provide a clearer visual of the sliding scale in total cost. For instance:
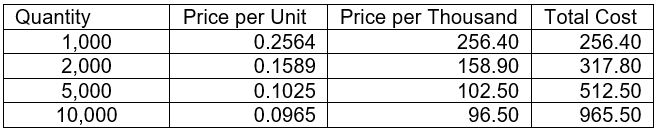
**Note: This chart does not reflect any pricing at Blue Label. For demonstration of pricing breakdown only**
So between 1,000 and 2,000, you can get twice the amount of labels for $61.40 more. The ‘Price per Thousand’ (sometimes notated as ‘Price per M’) category is intended to give a more clear ‘apples to apples’ comparison on items that have a small unit price.
The Factors That Impact Beer Label Costs for Craft Brewers
As a digital label printing company, we gather a lot of information to estimate the overall cost for your beer label project. There are multiple factors that can impact your costs. These factors include:
- Product type
- Material
- Size
- Quantity
- Multiple versions
- Lamination / varnish
- Tooling
- Decoration
- Application
- Variable content
Product type
The very first step in the pricing process is to determine what you want to accomplish with your beer labels. Depending on your product, design, and environment, you may be in the market for pressure sensitive labels, shrink sleeves, double sided labels, or hang tags.
For example, shrink sleeves have a special production process and may require certain quantities to help maximize your invest in them. Meanwhile, pressure sensitive labels have a multitude of material options and decorating capabilities that can be applied to them. Our experts can offer advice on which label type is ideal for your brewery.
Material
Your label material of choice is going to be a notable contributor to your overall label costs. Each label is made with multiple layers that include a top layer (face stock) , an adhesive, and a liner. Some label materials will cost more per linear foot than others, so a more expensive material will lead to overall higher project costs.
When it comes to beer labels, there are two main types of material options: film and stock paper. Films for pressure sensitive labels are a natural choice as they’re more resistant to fluids.
Paper materials can provide a distinct look for beer containers, but can be two to five times more expensive than standard semigloss or white BOPP films. Given that materials make up a significant percentage of your total beer label costs, that distinctive paper material could lead to a cost increase of up to 40 percent overall.

Size
The overall size of your label is another major factor for beer label costs. Label size dictates how much material is required. Simply put, the more material we use, the more expensive your label project will be. As such, larger labels can cost more than smaller labels from a raw materials standpoint.
Print layout is also another major factor that can influence label sizing costs. Label materials come in long rolls that are fed through a machine that prints your design onto the face stock of the roll. Depending on the size of your design, you may be able to fit multiple labels across the width of the roll.
By fitting more labels on a roll, you can improve printing efficiency and limit label material waste. This amount of material waste isn’t too noticeable in smaller orders, but a 20 percent difference in material costs is a noticeable change for larger quantities of labels.
Fortunately, there are measures you can take to help maximize space and minimize waste. Work with your designer and printing company to adjust the size of your label, especially if a fraction of an inch is the difference between a 15 to 30 percent bump in material costs. Our Beer Sizing and Dimensions Guide also includes optimal measurements for the most cost-effective sizing for printing your beer labels.
Quantity
The total number of labels printed in a project has a massive impact on your final project price. As expected, projects with higher label quantities will have a higher total cost simply because they consume more material. However, there is a potential for savings that isn’t as straightforward as you may expect.
While digital label printing allows breweries the flexibility to invest in lower quantities of beer labels, higher quantity runs can help you drive down your cost per thousand. Every project includes initial costs to set up the printer, calibrate colors, set up die cutting, and complete other tasks to start the manufacturing process.
Regardless of whether you need 200 or 200,000 labels, we have to go through those same processes. However, that setup time can be amortized much more efficiently over a long print run of labels, which means that higher quantities of labels actually drive down label costs.
While larger quantities can drive costs down, there are some potential cost advantages of buying lower numbers of beer labels. Digital label printing allows you to avoid the hidden costs of labels of obsolescence – regulation changes, brand updates, and other events that can make your beer labels outdated. That flexibility can be very valuable when you’re dealing with future events that could lead to unnecessary label waste.
Multiple versions
One notable cost factor is the ability to group multiple label versions together in a single project. While plate-based printing will require added fees for each label version, digital label printing can group these different labels together as long as there are 500 copies of each.
Maybe you don’t can 50,000 of one flagship… but maybe you do can 10,000 of your top five beers and have some seasonal releases to add in as well. Instead of placing five separate orders of 10,000 labels, digital technology allows you to place one order of 50,000 labels to take advantage of the lower ‘per thousand’ unit cost. Since everything is done digitally, we have the ability to mix and match your various versions into one production run, which helps save on setup and minimize waste.
Lamination / varnish
Every beer label needs some form of print protection. The average beer label is going to face several potential issues. Fluids like water and beer can wreak havoc with paper labels. Shipping and handling can rub off ink without a laminate or varnish layer.
Standard laminates and varnishes aren’t an additional cost, as much as they are something that’s baked into your starting project price. Every film label project is made with some form of laminate, while wine stock papers will require a basic varnish. There are also decorative laminates and varnishes available as well for an additional cost. Finishes such as soft-touch or textured laminates can serve a dual role of protecting your beer labels while adding to the overall look and feel of your packaging.
Tooling costs
Beer label costs may also include tooling fees, but these can vary depending on your label design and how they’re printed. Older printing methods, like offset or flexographic printing, use unique sets of plates to create your beer labels. As such, you’ll need to pay for a new set of plates for every piece of artwork. Digital printing doesn’t require plates, which cuts out those costs and any additional lead time required to manufacture plates.
Custom label shapes can also add tooling costs. Specialized pieces of metal called dies are used to cut specific shapes out of label materials. While digital label printing companies often have a wide range of existing dies, specialty shapes may require a newly manufactured part.
Depending on the size and shape, a new die can cost around $200. Of course, that die will then be freely available for any future label runs. At Blue Label, we have dies for most standard beer sizes in-house and can provide them for no extra cost to our customers. Our Beer Sizing and Dimensions Guide can walk you through the options and provides visual aids.
Decoration
While your choice of material, label size, and total quantity are the three biggest factors for project price, label decoration can add some additional costs depending on your needs. These added features can enhance the look and feel of your beer labels, which can add to your overall price per thousand and lead times based on your desired decoration.
Digital finishing equipment can apply many different decorative elements to beer labels. Foil stamping presses special foils into your material to create a raised image that stands out from other labels. Embossing imprints a special pattern or image into the label material, creating a pattern that consumers can see and feel. Spot varnishes allow you to coat specific parts of your design to make those elements pop. Each of these finishes can help capture consumers’ attention for an added cost.
Application
Your application process can also impact the beer label pricing as well. Your exact application process determines a few different factors:
- Roll size
- Unwind
- Liner
Applicators can require a specific roll size or “Max OD” (Maximum Outer-Diameter). Your application process can determine how big the roll is, which can require more rewinding. Smaller rolls will also require your printing company to break your labels down into more manageable quantities for your machinery. These efforts won’t make for large changes in price for most customers, but they’re another potential reason why you might see an uptick in beer label pricing.
The required unwind can also affect potential cost efficiencies. The unwind determines which edge of the label first comes off the roll. This unwind can change how your printer needs to position your labels during printing. Depending on the dimensions of your label, that new positioning can yield a more or less efficient print layout.
Certain applicating equipment may also require a specific type of label backing. The backing, also called a liner, is the bottom layer of a pressure sensitive label. Applicators have sensors that read the label gaps during application, but certain sensors may only be able to read paper or film liners. As such, you may need to invest in a film liner which could slightly increase your project price if your applicator requires it.
Variable content
Variable data printing is another way that digital label printing allows you to change certain elements in a design without having to create entire new art files. Essentially, variable data printing utilizes a spreadsheet or some other file format to modify a variety of design elements, such as a headline, image, name, or color. Variable data printing can also incorporate variable images and patterns, allowing you to alternate or serialize label designs.
Variable data is a very useful tool for batch numbering, product tracking, or creating individualized items. It does require a good deal of setup and administration, so adding variable data printing to a label can increase costs.

Added Value Opportunities for Beer Labels
While there are several factors that can add to your overall project price, it’s important to also identify potential value opportunities as well. There are a lot of services that won’t show up on your bill, but can make a massive difference for your company. Each of the following factors can not only help your business save time and money, but also spare you from avoidable headaches when it’s time to invest in beer labels.
Artwork prep and readiness
Every beer label starts off as an art file before it’s printed. Unfortunately, there are a litany of artwork issues that can pose problems for your labels. Common concerns like incorrect file formats, low-res images, and improperly built bleeds will lead to problems with printed products without prior attention.
The level of artwork assistance depends on the label printing company. A lot of printers will charge you for that time to make sure your art is ready. Others will provide artwork prep for free and guide you through the printing process from start to finish.
Label printers can also provide press proofs for a small fee so that you have a physical example of your product before investing in the full run. Artwork can translate very differently from a computer screen to printed product. Though they might add a little time and money in the short term, artwork prep and press proofs can help avoid costly errors or artwork issues on a full production run.
Shipping and turnaround times
While shipping isn’t a part of the label production process, it’s important to keep it in mind for your overall label costs. You’ll want to examine the turnaround times and whether or not there will be any additional charges if you need your beer labels sooner than the standard turn-time and standard shipping propose. Blue Label commits to five-business day turnarounds, but others may tack on rush fees that range from $100 to $350 depending on how quickly you need your beer labels.
Customer service and satisfaction guarantees
We don’t live in a perfect world. At some point you will inevitably run into an issue, be it a misspelling in the artwork or color not translating properly. If these issues occur, it’s important to find a label printing partner that won’t leave you stranded with faulty packaging.
A good quality department won’t change your beer label bill, but it’s priceless when you do run into any issues. Evaluate potential printing companies to see if they have any warranties and satisfaction guarantees to make sure you’re not stuck with an improper print job. You’ll want to talk to a live, friendly label expert whenever you call with any questions or concerns. If a potential label printer limits access to real people, they might not be there when you do have any issues.
Internal resources
Customer service representatives aren’t the only resources that can help you out with your beer label project. Some label printing companies offer additional internal resources that can help add value without increasing the costs of your beer label.
For example, Blue Label has several helpful blog posts, resources, and guides available online to help you prepare your labels for success. In addition, our designer directory can help you find a designer who understands the intricacies of the beer market and can create the perfect custom beer label design for your products.

What Breweries Can Do to Help Control Beer Label Costs
Proper packaging is an important investment for any brewery. Unfortunately, there are scenarios where you may end up paying more for your labels than necessary. Situations such as last-minute orders or unforeseen problems can lead to extra charges or delayed shipments.
The best way to avoid these issues and control your beer label costs is to prepare early. The sooner you start talking with a label printing company about your needs, the better. This head start will allow you and the printing company to identify any potential issues, avoid expedited shipping, and have everything ready to go for when you actually need your beer labels. You can also ask for test rolls to ensure that your labels work with your applicating equipment ahead of time instead of troubleshooting problems at the last minute.
Order your labels ahead of time. As long as they are properly stored, label adhesives won’t lose effectiveness for several months. Because of this, you can have your labels shipped to you a week ahead of when your applicator arrives and stil be good to go. This will give you plenty of leeway and a lot less stress when it’s time to label your beer bottles or cans.
Finally, the best way to help you invest in the perfect beer labels for your products is to work with the right label printing company. At Blue Label, we promise to deliver unmatched quality and service to help you create the best, most cost-effective beer labels for your exact needs. Contact us today to talk about your next beer label project.